Previous slide
Next slide
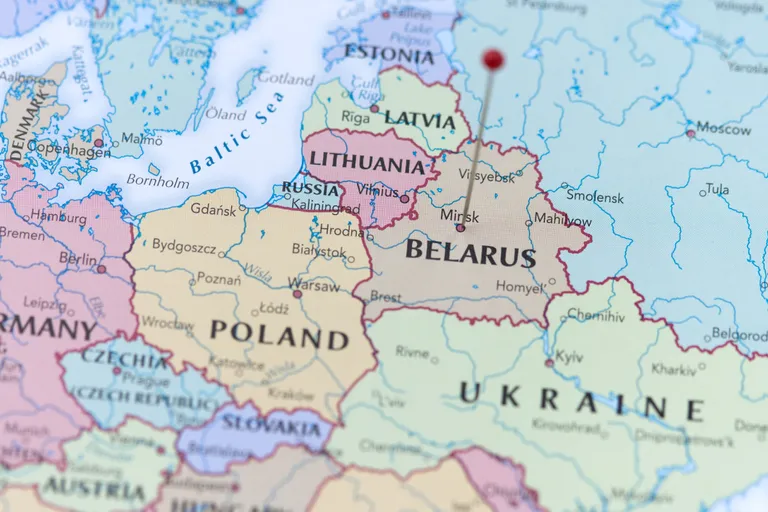
Belarus is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Below are some key details about Belarus:
Geography and Climate
- Capital: Minsk, the largest city and political, economic, and cultural hub of the country.
- Area: Approximately 207,600 square kilometers (about 80,200 square miles).
- Terrain: Mostly flat with large tracts of marshy land, and about 40% of the country is covered by forests.
- Climate: Belarus has a temperate-continental climate with cold winters and mild summers. The country experiences a significant amount of precipitation throughout the year.
Population and Language
- Population: About 9.4 million people (as of 2023).
- Ethnic Composition: Predominantly Belarusian, with minority groups including Russians, Poles, and Ukrainians.
- Official Languages: Belarusian and Russian. Russian is more commonly spoken in daily life.
- Religion: The majority of Belarusians are Eastern Orthodox Christians, with a minority practicing Roman Catholicism.
Government and Politics
- Political System: Belarus is a presidential republic. The President holds significant power, and the country has been under the leadership of Alexander Lukashenko since 1994.
- Administrative Divisions: The country is divided into six regions (oblasts) and the capital city of Minsk.
- International Relations: Belarus has close political and economic ties with Russia and is a member of several regional organizations, including the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU).
Economy
- Economic Structure: Belarus has a mixed economy, with significant state ownership in many sectors. The economy is heavily industrialized, with major industries including machinery, chemical products, agricultural products, and textiles.
- Currency: Belarusian Ruble (BYN).
- Trade: Belarus exports machinery, agricultural products, and energy (including refined oil products) and imports energy, machinery, and food products. Its main trading partners include Russia, the European Union, and Ukraine.
- Challenges: The economy faces challenges like dependency on Russia for energy, limited foreign investment, and economic sanctions from Western countries.
Culture and Society
- Heritage: Belarus has a rich cultural heritage influenced by both Eastern and Western Europe. The country has a strong tradition in folk music, dance, and literature.
- Education: The education system is well-developed, with compulsory education up to the age of 15. Higher education institutions are concentrated in Minsk and other large cities.
- Tourism: Belarus is known for its natural landscapes, historical sites, and Soviet-era architecture. The Brest Fortress, Mir Castle, and the Białowieża Forest are among the notable tourist attractions.
International Position and Recent Developments
- Relations with the West: Belarus’ relationship with Western countries has been strained due to issues like human rights concerns, lack of democratic reforms, and the suppression of political opposition.
- 2020 Protests: The 2020 presidential election, widely criticized as fraudulent, sparked mass protests and international condemnation. The government responded with a crackdown on opposition and dissent, leading to ongoing tensions.
- Sanctions: In response to these events, Western countries have imposed economic sanctions on Belarus, affecting its international trade and financial sectors.
Belarus remains a country with a unique position in Europe, balancing its historical ties with Russia and its complex relations with the West.
Belarus experiences a temperate-continental climate, characterized by distinct seasons. Here’s an overview of the weather throughout the year:
Winter (December to February)
- Temperature: Winters are cold, with temperatures often ranging from -4°C to -8°C (24°F to 18°F), though it can drop much lower during cold spells.
- Snow: Snowfall is common, and snow cover can persist for several months, especially in the northern regions.
- Daylight: Days are short, with limited sunlight.
Spring (March to May)
- Temperature: Spring starts chilly, with temperatures gradually rising from around 0°C (32°F) in March to 10°C-15°C (50°F-59°F) by May.
- Weather: Spring can be unpredictable, with frequent rain showers and occasional frosts early in the season.
- Nature: The landscape becomes greener, with flowers blooming and trees budding.
Summer (June to August)
- Temperature: Summers are mild to warm, with temperatures typically ranging from 18°C to 25°C (64°F to 77°F), although heatwaves can push temperatures above 30°C (86°F).
- Weather: This is the wettest season, with occasional thunderstorms, but also plenty of sunny days.
- Daylight: Days are long, with up to 18 hours of daylight in June.
Autumn (September to November)
- Temperature: Autumn sees a gradual cooling, with temperatures decreasing from around 15°C (59°F) in September to near freezing by November.
- Weather: The season is marked by increasing rainfall, fog, and the first frosts by late October or November.
- Foliage: Autumn is known for its beautiful fall foliage, especially in the forests and countryside.
General Weather Patterns
- Precipitation: Belarus receives a moderate amount of rainfall throughout the year, averaging about 600-700 mm (24-28 inches) annually. Rain is fairly evenly distributed, but summer tends to be the wettest season.
- Wind: The country experiences moderate winds, with stronger winds typically occurring in the winter.
